Adeno-Associated VIRUS (AAV) Services
As cell and gene therapy research continues to advance across a wide-range of diseases, the need for effective vectors for successful therapy delivery has increased. Identified as an optimal vehicle, adeno-associated virus (AAV) plasmids are the leading viral vector used in in vivo gene therapy clinical trials due to their high efficiency and enhanced safety in humans.
As a global leader in genomics services, GENEWIZ has developed unique AAV-ITR sequencing, AAV plasmid synthesis, AAV packaging and AAV plasmid preparation capabilities to support scientists in their in vivo gene therapy research. GENEWIZ’s ground-breaking AAV services also include sequence verification and correction of inverted terminal repeat (ITR) regions, which are crucial for rAAV packaging production.
AAV Services
AAV-ITR Sequencing
Utilizes Sanger protocols to sequence-confirm difficult ITR regions, expediting screening and validation of lead candidates. Whole AAV plasmid sequencing through primer walking is also available.
AAV Packaging
Unlock the full potential of cell or gene therapy by overcoming the instability of AAV vectors with GENEWIZ’s AAV packaging workflow. Our proprietary AAV plasmid synthesis process offers industry-leading project quality, completion time, and flexibility, ensuring researchers can harness the powerful benefits of this technology effectively.
AAV ADVANTAGES
AAV SYSTEM
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is one of the most actively investigated gene therapy vehicles. AAV has a linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genome of approximately 4.7 kilobases (kb), with two 145 nucleotide-long inverted terminal repeats (ITR) at the termini which are crucial for rAAV production.
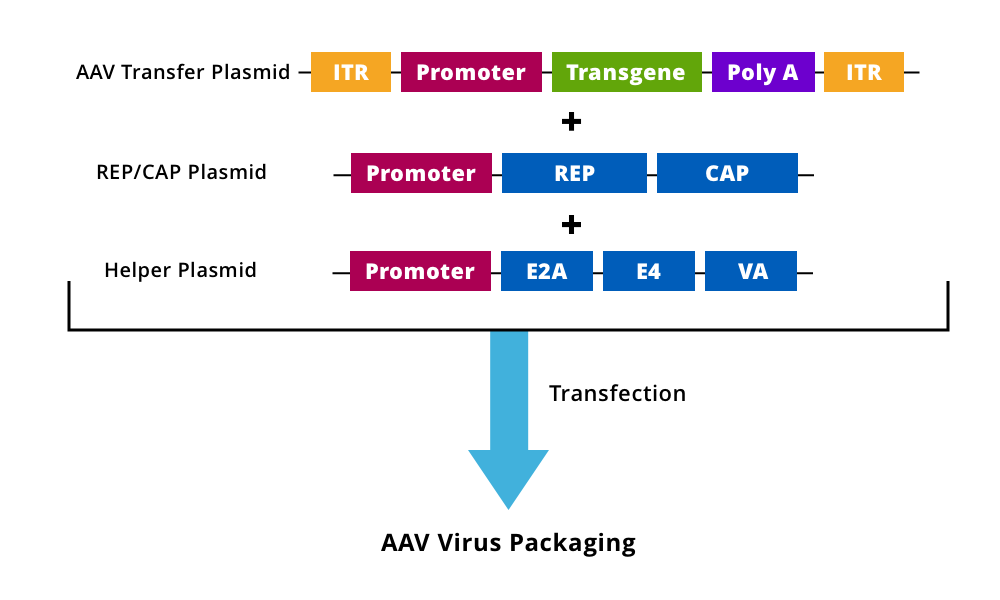
Figure 1. An AAV transfer plasmid containing the modified/transgene expression cassette with intact ITRs is generated and cloned into a plasmid along with Rep/Cap and helper plasmids, which are co-transfected into cell lines for virus packaging and rAAV production.
Features & Benefits
-
Rapid Turnaround TimesStarting at just 5 business days -
Real-Time Project UpdatesThrough our online system -
Ph.D.-Level Project ManagersAvailable at each step
Technical Resources

Tech Note: Reading Through the Inverted Terminal Repeats (ITRs) of Adeno-associated Virus (AAV)
GENEWIZ has developed a high-quality, direct Sanger sequencing method that reads through both intact and commonly mutated inverted terminal repeat (ITR) regions of adeno-associated virus (AAV). This method is an effective tool for assessing the integrity of ITRs in AAV plasmids.

Tech Note: An Efficient and Reliable Approach to AAV Packaging
While AAV is a powerful vehicle for gene delivery, unstable ITRs threaten the fidelity of rAAV genomes. Loss of ITR integrity diminishes the packaging efficiency of rAAV particles and thus viral titer. In this tech note, discover the effect of partial and full ITR deletions on AAV packaging and how to reliably identify and effectively correct them.