Codon Optimization
As experts in synthetic DNA, we understand the importance of accurate gene synthesis and its subsequent expression, particularly in heterologous systems. A multitude of factors, including codon bias, can affect the transcriptional and translational efficiency of a gene in a host organism. GENEWIZ’s codon optimization tool considers these critical factors to produce codon optimized gene sequences for efficient expression in almost all host systems.
Codon Optimized Synthetic GENES
Codons represent the genetic code that transfers information from genes to mRNA to protein. Both redundancy and evolutionary constraints, including the availability of tRNA isoacceptors, TATA box, Shine-Dalgarno sequences, and more, result in preferential usage of one codon over another for the same amino acid. This phenomenon is known as codon bias.
Codon optimization is a process used to improve gene expression and increase the translational efficiency of a gene of interest by accommodating codon bias of the host organism.
Download your complimentary copy of our tech note, Enhancing Protein Expression by Leveraging Codon Optimization, to learn how you can leverage GENEWIZ’s free codon optimization tool to enhance your protein expression.
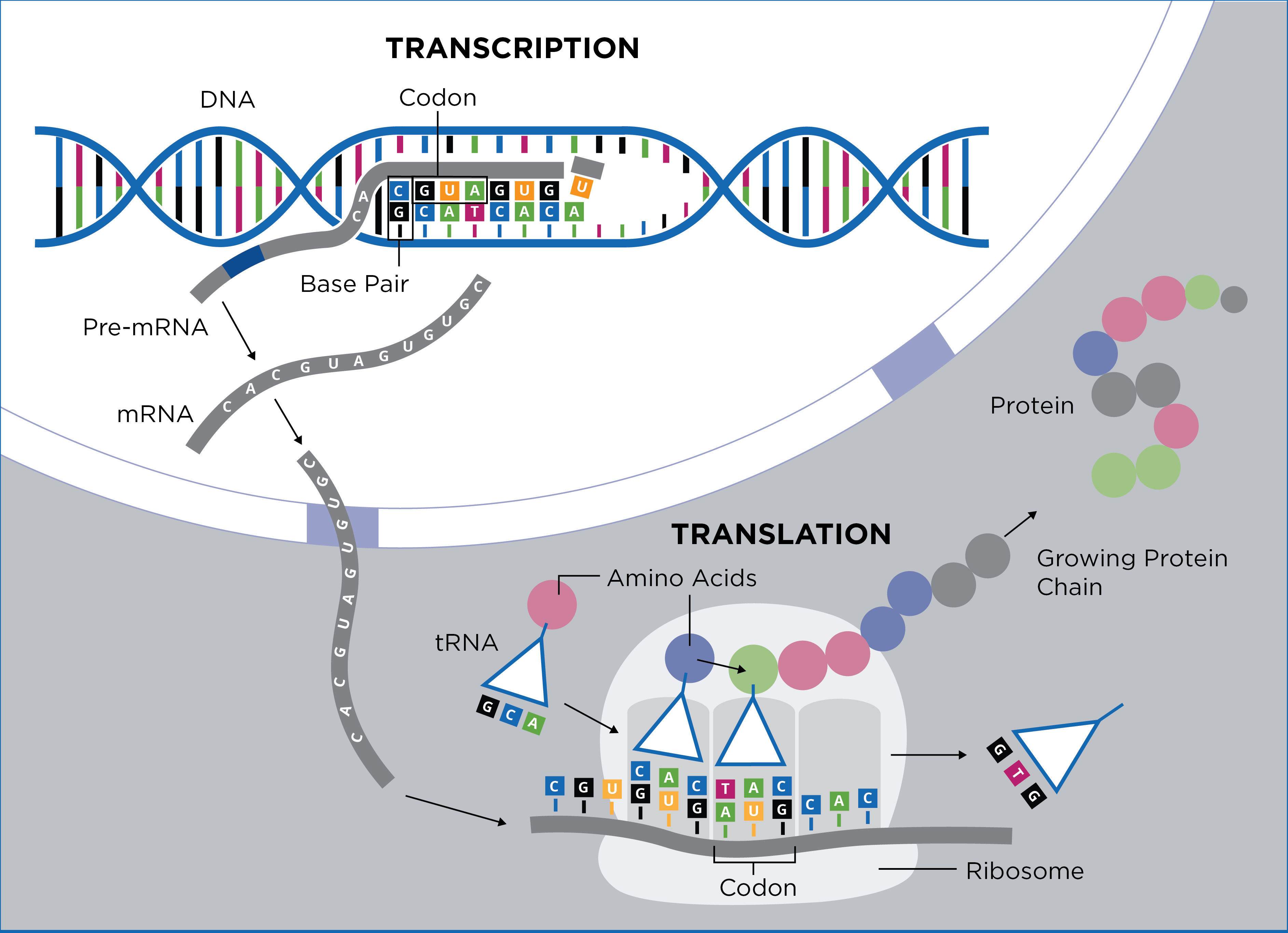
Schematic representation of protein expression
Optimize and Order In Minutes
The introduction of optimization algorithms, a type of artificial intelligence, has significantly streamlined the process of designing a DNA sequence to optimize protein expression in target organisms. When you partner with GENEWIZ, you get access to our free codon optimization algorithm tool that recognizes and optimizes key parameters to stabilize DNA sequences and improve gene expression. Choose from dozens of expression systems and hundreds of restriction enzyme sites while we ensure that your sequence is tailored to your research project.
